About Ashland University
Founded in 1878 as Ashland College, the name of the institution was changed to Ashland University in 1989 to reflect the many diverse undergraduate, graduate and professional programs offered.
Ashland continues to have a rich tradition as a private, comprehensive institution preparing students for exciting professions and careers. The university consists of four academic colleges - the College of Arts & Sciences, Dauch College of Business & Economics, Schar College of Education and Schar College of Nursing and Health Sciences - as well as Ashland Theological Seminary.
Ashland University places great emphasis on the importance of each individual. The phrase “Accent on the Individual” has been an AU core value for many years and characterizes well the nature and content of the campus environment. It means that our concern for the student extends beyond ensuring a quality education in the classroom and laboratory to include a commitment to provide a stimulating and supportive environment in every respect. These ideas must be evidenced daily in the classroom, residence halls, each teaching site, on the playing fields and in our interaction with others.
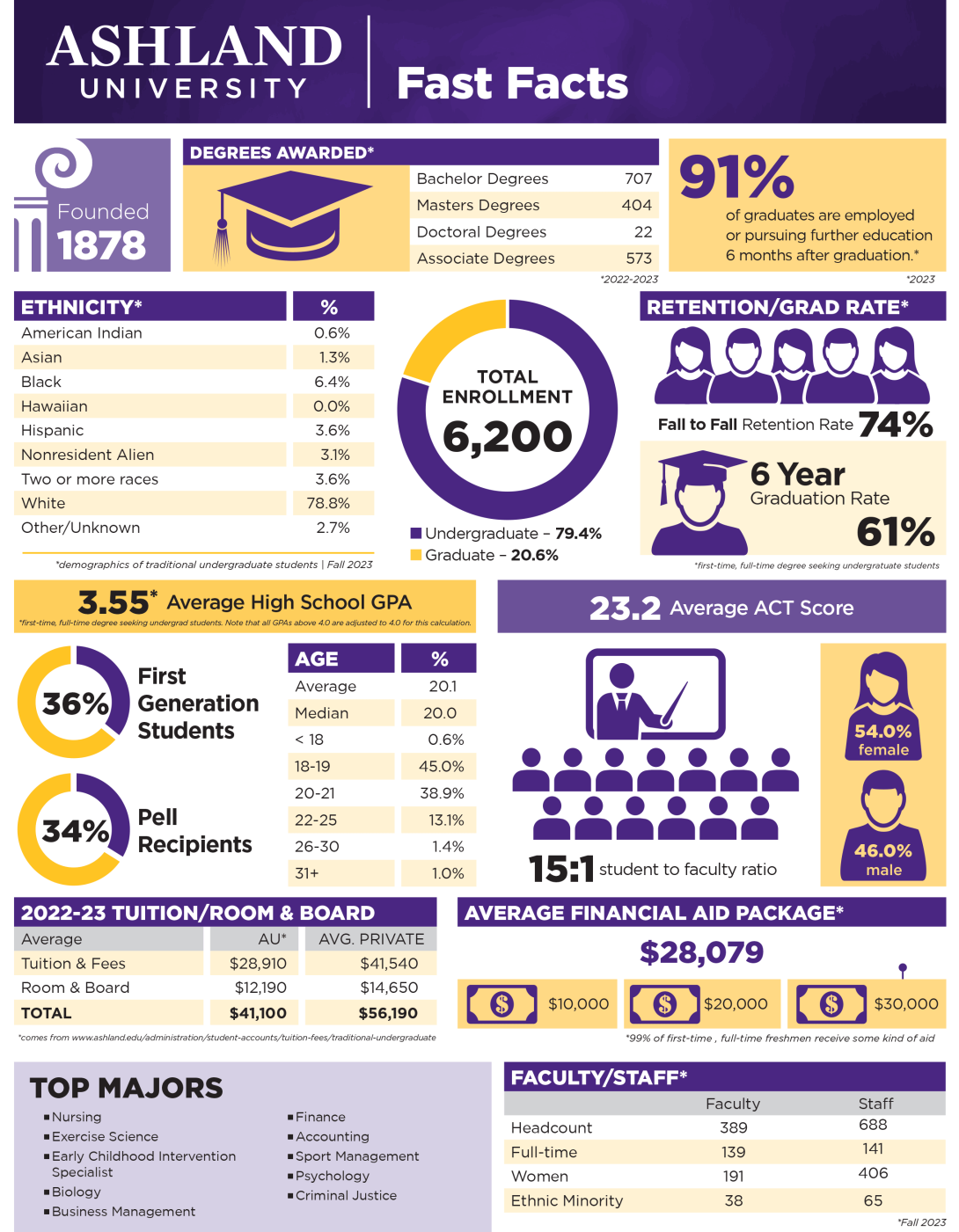
AU Fast Facts
Mission
Ashland University, guided by our Christian heritage, is a comprehensive, private university that provides a transformative learning experience, shaping graduates who work, serve and lead with integrity in their local, national and global communities.

Vision
Ashland University aspires to be a nationally recognized, private university where traditions of excellence are fostered and students discern their life calling and thrive.

Core Values
Accent on the Individual - Pledges the best individual and collective efforts to challenge and encourage each member of the university within a supportive community.
Spirituality and Faith - Affirms Christian values as a core element of the university's institutional identity, emphasizing faith in God, moral integrity and respect for the diversity of values and faith of each person in a community of learning.
Character Development - Promotes integrity, self-discipline, responsibility, compassion, leadership, service and good citizenship.
Academic Freedom - Supports free, open and critical inquiry for both students and faculty necessary for intellectual and professional development.
Excellence in Teaching - Emphasizes teaching supported by research and scholarship as the university's central responsibility.

Supporting Individual Growth
Ashland University supports equal opportunity and access to higher education. We strive to offer an educational experience that is inclusive of people of all religions, races, ethnicities, genders, ages and sexual orientations, as well as people with disabilities. We work to provide not only a quality education, but also a diverse and multicultural one.
In addition, we encourage student individuality and the free, open and critical inquiry for students and faculty that is necessary for intellectual and professional development. Having officially endorsed the Chicago Statement in 2017, AU firmly believes in the freedom of expression and is fully committed to continuing our full and unwavering support to protect students and faculty members' academic freedom and freedom of speech on campus.